MASH resolution with no worsening of liver fibrosis demonstrated by semaglutide: Interim results from the phase 3 ESSENCE trial
10 Apr 2024
Share
STUDY DESIGN
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) is a chronic and progressive liver disease characterized by hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis.1 Despite its high prevalence, effective pharmacological treatments remain limited, with current strategies primarily targeting weight reduction and glycemic control.1 Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), has been extensively studied in a broad spectrum of cardiometabolic diseases, positioning it as a potential therapeutic option for MASH.1
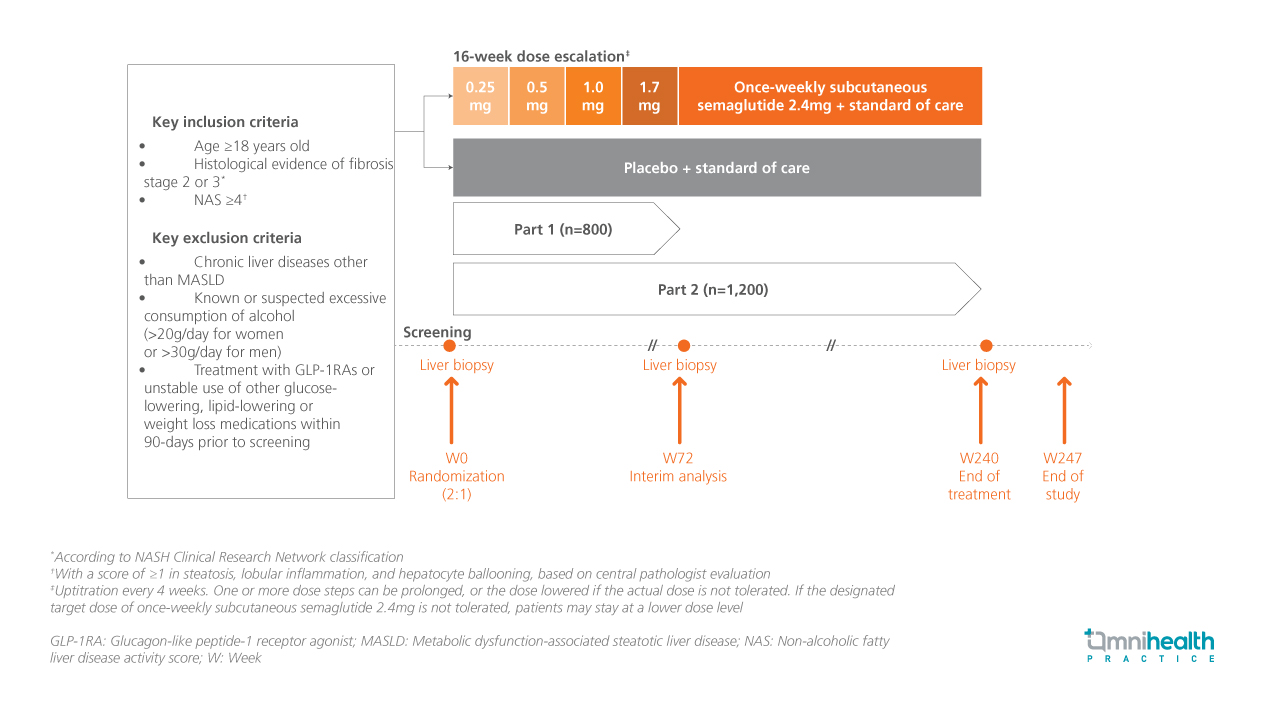
The ESSENCE trial is an ongoing, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study assessing the efficacy and safety of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4mg in patients with biopsy-confirmed MASH and fibrosis stages 2-3.1 In part 1 of the study (0-72 weeks), participants (n=800) were randomized 2:1 to receive semaglutide (n=534) or placebo (n=266) along with standard of care.1 The primary analysis was conducted on the intention-to-treat (ITT) population after 72 weeks.1 The primary endpoints of part 1 of the study included steatohepatitis resolution without worsening of liver fibrosis and liver fibrosis improvement without worsening of steatohepatitis.1 Confirmatory secondary endpoints were change in body weight, resolution of steatohepatitis with improvement in liver fibrosis, and improvement in SF-36 bodily pain.1
FINDINGS
| Primary endpoints: |
|
|
|
| Secondary endpoints: |
|
|
|
|
| Safety: |
|
|
|
|
“Semaglutide demonstrated a safety profile consistent with previous phase 2 MASH trials and the large body of evidence for semaglutide in other indications”
Professor Philip N. Newsome
Roger Williams Institute of Liver Studies,
Faculty of Life Sciences and Medicine,
King’s College London,
Foundation for Liver Research, and King’s College Hospital,
London, United Kingdom
References
- Newsome PN, et al. Phase 3 ESSENCE trial: Semaglutide in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. Presented at the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) Annual Meeting 2024; November 15-19, 2024.